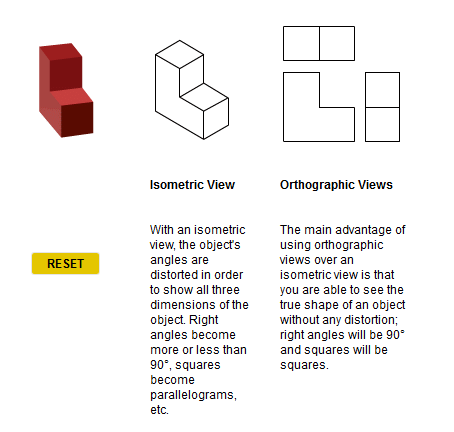
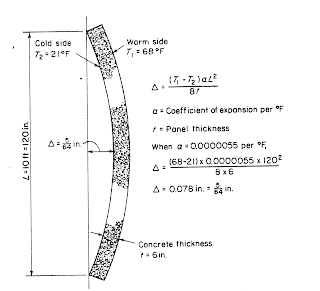
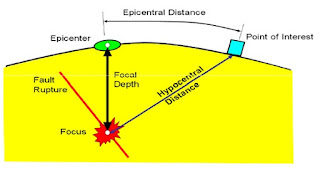
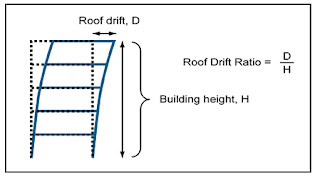
Strain Energy
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Beams/Strain_Energy.html Strain Energy The external work done on an elastic member in causing it to distort from its unstressed state is transformed into strain energy which is a form of potential energy. The strain energy in the form of elastic deformation is mostly recoverable in the form of mechanical work. Nomenclature c = distance from neutral axis to outer fibre(m) E = Young's Modulus (N/m 2 ) F = Axial Force (N) G = Modulus of Rigidity (N/m 2 )(m) I = Moment of Inertia (m 4 )(m) l = length (m) M = moment (Nm) V = Traverse Shear force Force (N) x = distance from along beam (m) z = distance from neutral (m) γ = Angular strain = δ/l δ = deflection (m) τ = shear stress (N/m 2 ) τ max = Max shear stress (N/m 2 ) θ = Deflection (radians) Strain Energy Pure Tension and compression Strain Energy Pure Torsion Strain Energy Direct Shear Alternatively allowing z to be a variable:....